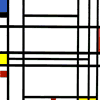
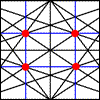
This is an analysis of the expressiveness power of the positions of the shapes in a picture, and how they gain dynamism, stability, rhythm, order, disorder, etc.. depending on how they are arranged.
Some basic types of positions of the forms in a plane:
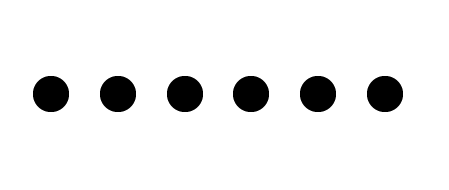
1. Horizontal alignment of the forms.
We can see this by placing the same or similar shapes along a horizontal, in a repeated way. The distance between elements will make a rhythmic repetition more or less fast. If the elements are very separated it will cost more to relate them to each other.
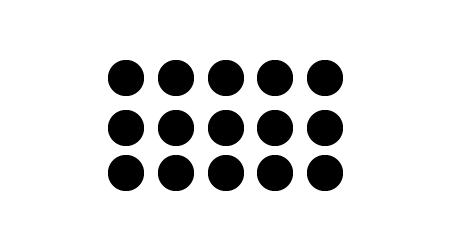
2.The Aggregation / Compression of shapes
Individual but aligned shapes that seem a homogenous group, because of the closeness between them. The group has a static aspect.
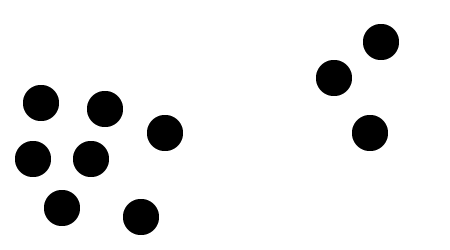
3.The dispersion of shapes.
The shapes appear in different places so that they can not be easily grouped. The dispersion produces a dynamic effect.
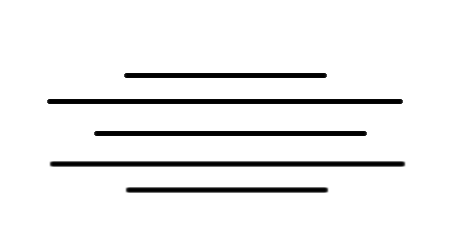
4.Symmetrical shapes.
Disposition with a lateral symmetry of the individual elements, respect to a vertical and horizontal axis. Symmetry produces a static effect.
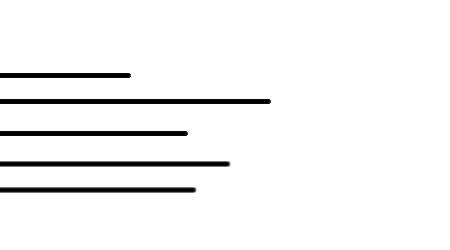
5.Asymmetry.
For example, all the elements aligned to the left side. As the right side is empty, there is an asymmetry or imbalance.
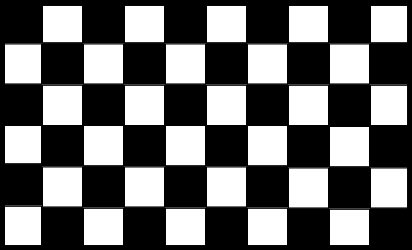
6.The grid
Division of the polane through the forms into a structure with regular parties repeated. It makes an order effect and it´s the basis for a widescreen design.
7.The structure, texture and pattern.
These three elements generate an internal order which generates relationships of similar forms.